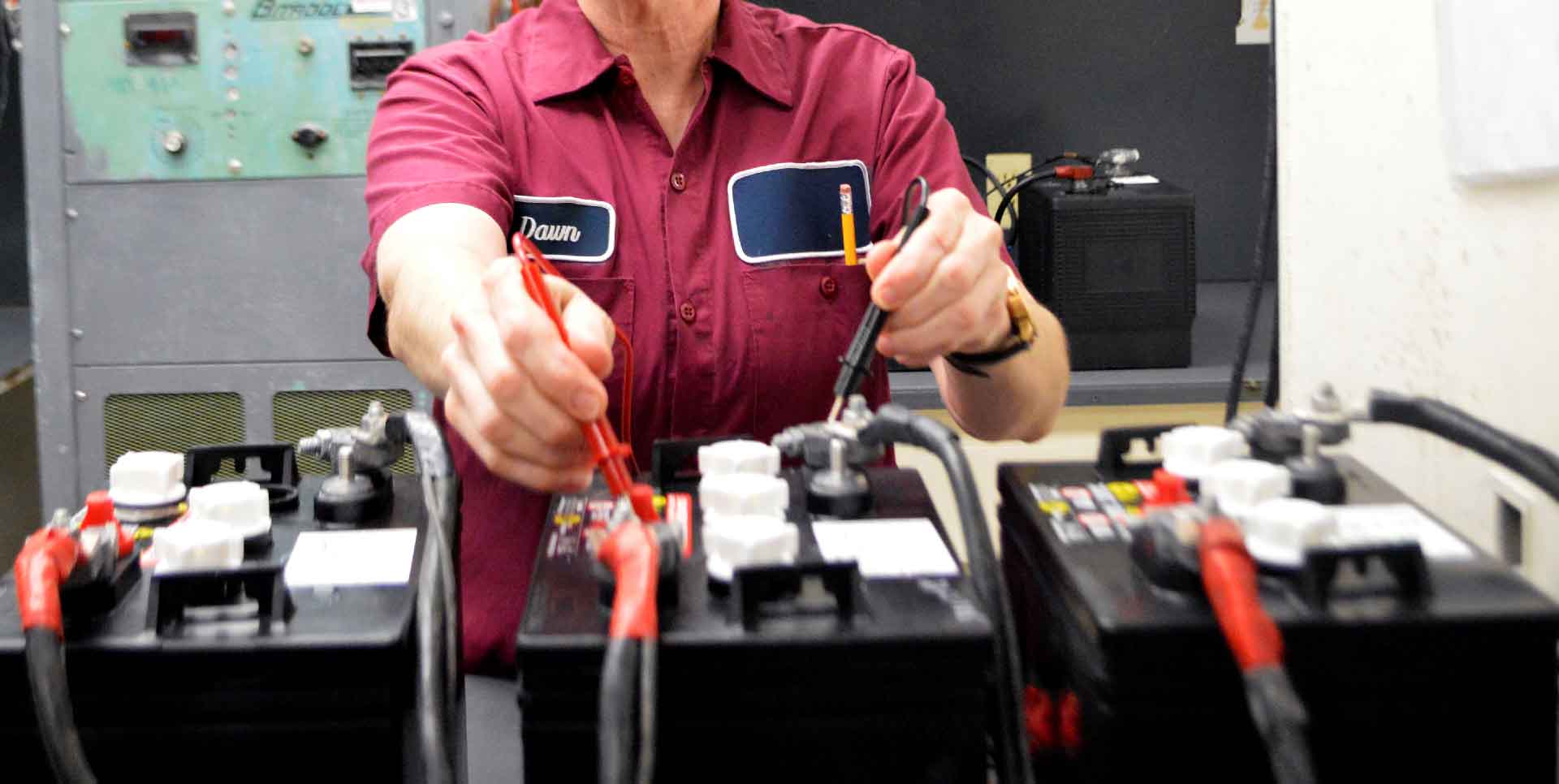
It’s important to maintain the batteries that keep your machines and vehicles running. You already know that proper charging techniques are essential when it comes to battery maintenance, but do you know the things will kill your battery?
Whether you're using AGM or Flooded batteries, there are surefire ways that will knock the life out of your battery no matter what type you’re using. By simply avoiding many of these actions, you can add life to your battery.
Overcharging
Charging a battery past 100% can compromise the integrity of your battery and shorten its service life. Overcharging or continuously charging can:
- Cause corrosion of the positive battery plates
- Increase battery water consumption
- Increase the internal temperatures, which can lead to heat damage that is beyond repair
Different types of batteries can be more sensitive too overcharging and experience different forms of damage. Sealed lead-acid (SLA) and gel batteries, for example, are particularly susceptible to overcharging damage because any lost water cannot be replaced. While overcharging a lead-acid batteries, causes the electrolyte water to break into oxygen and hydrogen gas, which depletes electrolyte levels in the batteries. This causes the concentration of the sulfuric acid in the electrolyte increases, which then damages the battery plates and reduces battery life.
Undercharging
Both overcharging and undercharging a battery can cause battery damage. If you don’t leave the battery on the charger until it’s fully charged, the battery will drain faster. For example, undercharging a lead-acid battery causes plate sulfation in which the sulfuric acid reacts with the plates to form lead sulfate crystals. This reduces the ability of the battery to accept a full charge, and undercharging worsens, which can lead to premature battery failure.
Extreme Discharge
For most batteries, it is recommended you do not let them drop all the way to 0% charge. In fact, for most batteries, you shouldn’t let them drop below 30-50%. It is especially important to not store a battery with a depleted charge. If you are not using your battery long periods of time, it’s still important to check the charge periodically as a non-used battery will lose its charge over time.
Sulfation
Sulfation is the number one reason you should not store your battery with an empty charge. When a battery is empty, white sulphuric crystals appear on the lead plates and will prevent the battery from holding a charge. Once sulfation of the lead plates has occurred, reversing the effects is highly unlikely. So it is critical to take care of your batteries from the start.
Extreme Temperatures
Although AGM batteries do better in extreme temperatures than Flooded batteries, very high and low temperatures can damage batteries. Because of the loose liquid in a Flooded battery, temperatures extremes can, especially if prolonged, shorten the life of a battery by freezing or evaporating that liquid.
Seasonal Storage
During the off-season for your equipment, you need to take a couple simple steps to avoid damage to your battery. Disconnect the battery's negative cable (or remove from the equipment) and charge the battery to a full charge condition.
Be sure to inspect fluid levels both before and after charging. Note: deep cycle batteries should not be maintained with traditional offseason charging if you are unable to inspect fluid levels on a monthly basis.
While these are just a few things that will contribute to a short battery life, it’s important to consult the instruction manual or talk to your battery provider to make sure you can get the best life out of your battery.